Brief Introduction to RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation)
Imagine this, you are the owner of a company, and your company has a customer service department, the customer service department is responsible for all customer request and complaint about the product the company has to offer and it even goes beyond that, the customer service department ensures that customers have a seamless experience with the company’s products or services from the moment they inquire about them to after-sales support. The team handles inquiries, resolves issues, provides product information, offers technical support, and gathers feedback to continually improve the customer experience. They serve as the bridge between the customers and the company, fostering trust, loyalty, and satisfaction. To ensure efficiency and effectiveness, the customer service department utilizes various tools and technologies, implements best practices, and continuously trains its staff to deliver exceptional service.
Now, with all that context built up, imagine doing all that with a Large Language model (LLM), yeah at first you may think of ChatGPT and its likes, but there is a more powerful technology that can be built on top of these LLM’s, and it is called RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation). That’s just one idea, literally just scratching the surface.
RAG core function is to bridge the gap between powerful large language models and real-world knowledge and closed data sources. With the scenario painted above, if the company product database was somehow fed into the LLM to create a chatbot which would be used alongside the customer support, don’t you think the company will have a more robust and less churn from the customers.
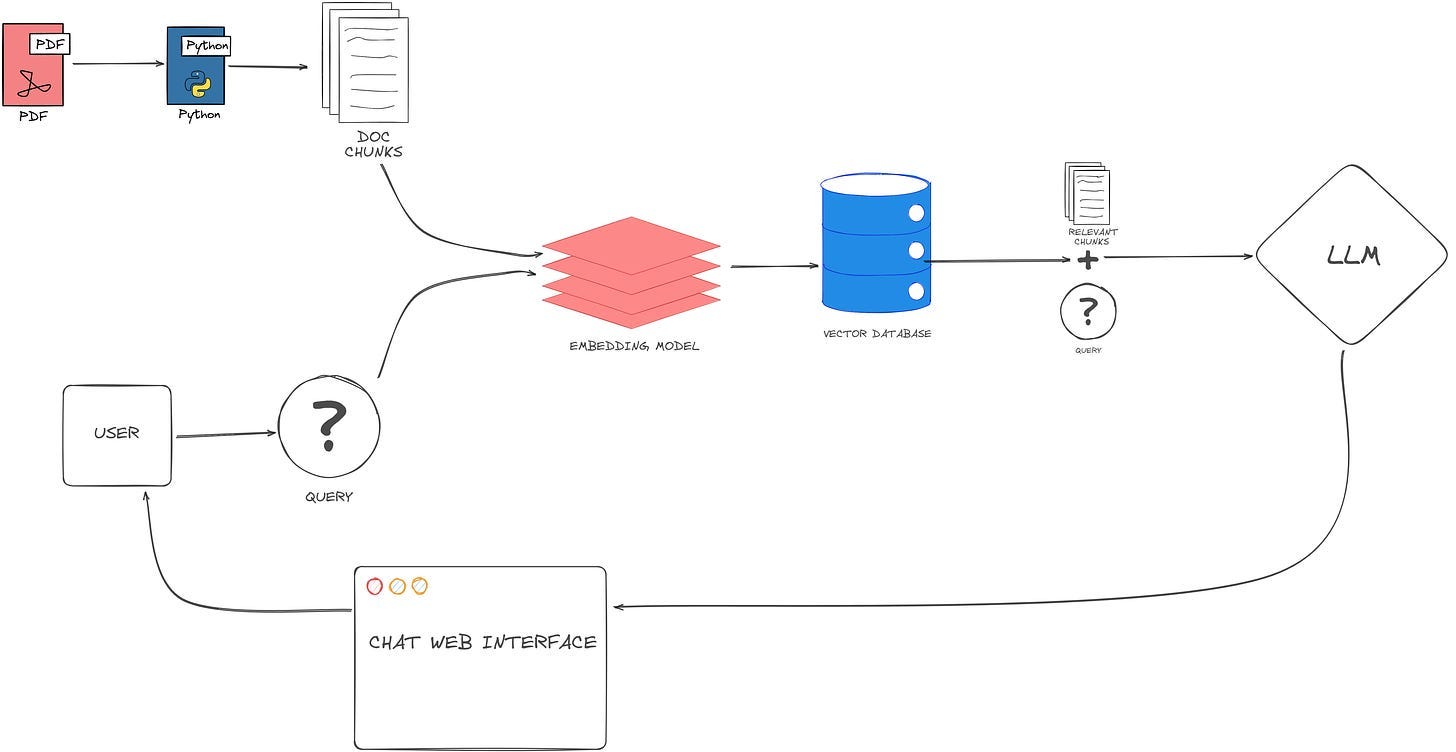
A basic RAG architecture consists of 5 key steps, Data Collection and Preparation, Data Chunking, Document Embedding, Query Encoding and Retrieval, Language Model integration.
Data Collection and Preparation
This first step is gathering relevant data sources for the relevant target use case, and this can include any type of document or database, in the diagram, i just used a PDF to illustrate. Additionally, software tools like Langchain and Llama Index are very helpful in this process. Langchain facilitates the extraction of valuable insights from unstructured text data, enabling efficient analysis of documents, articles, and other textual sources. On the other hand, Llama Index provides comprehensive indexing and search capabilities, allowing users to quickly locate and access relevant information across multiple databases and repositories. By leveraging these advanced technologies, the company can streamline the data gathering process, ensuring that they have access to the necessary information to drive informed decision-making and achieve their objectives.
Data Chunking
This second step involves breaking down the gathered data into manageable chunks or segments. Data chunking is crucial for handling large volumes of information effectively, especially when dealing with lengthy documents or extensive datasets. By breaking the data into smaller chunks, it becomes more manageable for further processing and analysis in subsequent steps of the RAG architecture.
Data chunking can be approached in various ways depending on the nature of the data and the specific use case. For text data, it may involve segmenting documents into paragraphs, sentences, or even smaller units such as phrases or keywords. For structured data, chunking may involve partitioning datasets into subsets based on specific criteria or attributes.
The goal of data chunking is to facilitate efficient processing and analysis by organizing the data into meaningful units that can be easily handled and manipulated. This step lays the groundwork for subsequent stages such as document embedding and query encoding, enabling the system to extract relevant information and generate accurate responses effectively.
In the context of the RAG architecture, data chunking plays a critical role in preparing the data for further processing and integration into the overall knowledge retrieval and generation framework. By breaking down the data into manageable chunks, the system can effectively handle diverse sources of information and provide more accurate and relevant responses to user queries.
Document Embedding
Document Embedding is a pivotal stage within the RAG architecture, constituting the third step in the process. Here, textual documents undergo transformation into numerical vectors within a high-dimensional space, a technique known as document embedding. This transformation captures nuanced semantic and contextual information embedded within the text, facilitating efficient comparison and retrieval of pertinent information.
Once documents are embedded into vector representations, similarity metrics like cosine similarity or Euclidean distance are employed to gauge the likeness between documents or between a user query and documents in the corpus. This empowers the system to retrieve documents that exhibit semantic similarity to the user query, enabling seamless knowledge retrieval and generation. By embracing document embedding techniques, the RAG architecture enhances the system’s ability to comprehend the semantic context of user inquiries and extract relevant information from a wide array of textual sources, thus elevating the accuracy and relevance of generated responses.
Query Encoding and Retrieval → Language Model integration.
Query Encoding involves transforming user queries into numerical representations within the same vector space as the document embeddings. This encoding process ensures that user queries are effectively matched against the embedded documents, enabling the system to retrieve relevant information accurately. Various techniques, such as tokenization, embedding, and encoding, are utilized to convert natural language queries into numerical vectors that capture their semantic meaning and context.
Once queries are encoded, they are integrated with the document embeddings through a language model, typically a large pre-trained model like BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers). This integration step enables the system to understand the relationships between the user query and the embedded documents, facilitating accurate retrieval and generation of responses. The language model leverages the encoded queries and document embeddings to generate contextually relevant responses, ensuring that the retrieved information aligns with the user’s intent and requirements.
By combining query encoding with language model integration, the RAG architecture enables seamless interaction between users and the system, allowing for efficient knowledge retrieval and generation. This integration of advanced natural language processing techniques enhances the system’s ability to understand and respond to user queries effectively, ultimately improving the overall user experience and satisfaction.
Thanks for reading this article, if you are interested in more things like this, you can subscribe to my substack here.